Q
What model of Isuzu MU-X rear differential oil is used
When it comes to choosing rear differential oil for your Isuzu MU-X, it's recommended to use API GL-5 specification gear oil with an 85W-90 viscosity rating. This is the standard requirement for the rear axles of most Isuzu models, as it effectively protects the gears by ensuring proper lubrication and wear resistance even under heavy loads. For the exact product model, refer to your owner's manual or consult an authorized Isuzu service center to make sure it perfectly matches your vehicle's year and configuration.
To expand a bit, selecting the right gear oil boils down to two key factors: viscosity grade and API classification. The 85W-90 rating works well with Malaysia's tropical climate, while GL-5 is specifically formulated to handle the high-pressure conditions of rear differential gear sets. If you frequently tow heavy loads or go off-roading, consider using fully synthetic gear oil for enhanced durability.
Regular gear oil changes – typically every 40,000 to 60,000 kilometers – are crucial for extending the lifespan of your rear differential. Also, check the oil seals for leaks to prevent contaminants from entering and causing gear damage. While other models like the Toyota Fortuner or Mitsubishi Triton may have similar rear differential oil specifications, additive formulas can vary between brands, so mixing different oils isn't advisable. As always, prioritizing the manufacturer's recommendations is the best practice.
Special Disclaimer: This content is published by users and does not represent the views or position of PCauto.
Related Q&A
Q
how much is Isuzu MU-X
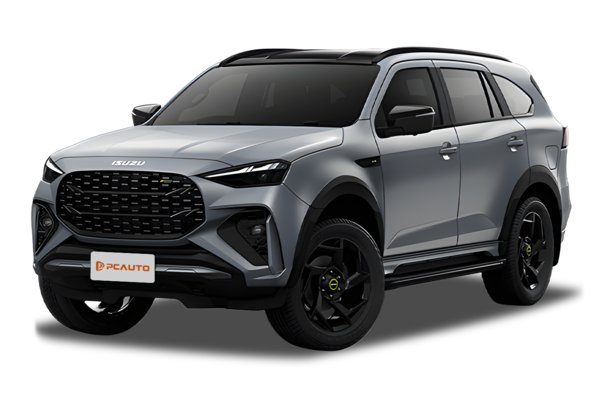
In the current Malaysian market, the Isuzu MU-X ranges roughly from RM 169,000 to RM 208,000, depending on the variant and specs. Keep in mind, actual prices might shift a bit with dealer promotions or optional extras, so your best bet is to hit up your nearest authorized Isuzu dealer for the latest numbers.
As a 7-seater SUV, the MU-X has built a solid rep for its tough chassis and reliable diesel heart. Under the hood, you'll find the 3.0L Blue Power turbo diesel engine, which dishes out great low-end torque and impressive fuel economy—perfect for Malaysian families tackling long highway drives or the occasional light off-road adventure.
Safety hasn't been skimped on either, with features like electronic stability control, multiple airbags, and a reverse camera all part of the package. Inside, it's all about practicality: there's plenty of room for passengers, and the seats fold in all sorts of ways to juggle people and cargo.
One thing worth mentioning is that the MU-X holds its value pretty well in the used car market. That's probably down to Isuzu's strong reputation for durability, especially from their commercial vehicle roots. If your budget's a bit tight, a well-maintained second-hand MU-X could be a smart alternative to consider.
Q
Isuzu MU-X how many seats
The Isuzu MU-X is a popular 7-seater SUV in the Malaysian market, perfect for family trips or when you need to carry a crowd. It's got that classic 2+3+2 seating setup – fold down the second row and you'll free up more luggage space, while the third row works well for kids or adults on shorter rides. What really stands out about this SUV is its tough chassis and reliable diesel engine, which make it a solid performer for Malaysia's varied road conditions – whether you're cruising around the city or tackling some light off-roading, it handles it all with ease. Safety-wise, the MU-X doesn't skimp either, coming with features like electronic stability control and multiple airbags to keep everyone on board protected. For Malaysian buyers eyeing a 7-seater SUV, the MU-X is a practical and budget-friendly pick. It offers plenty of room for passengers, impressive fuel efficiency, and low maintenance costs – ideal for folks who need to balance family needs with everyday usability. Plus, Isuzu has a wide after-sales service network across Malaysia, which adds extra convenience for owners down the line.
Q
When did Isuzu MU-X start
The Isuzu MU-X first hit the scene back in 2013, making its debut in Thailand before rolling into Malaysian showrooms the following year, 2014. Slotted in as Isuzu's flagship seven-seater SUV for Southeast Asia, it stepped up to replace the outgoing Isuzu Alterra. Built tough on the D-Max pickup platform, the MU-X carries forward Isuzu's rock-solid reputation in diesel engine tech, packing either a 3.0-liter or 1.9-liter turbo diesel under the hood. These engines dish out impressive fuel efficiency and that legendary Isuzu durability, making it a perfect fit for Malaysia's long highway stretches and those trickier, rough-and-tumble roads.
Over the years, Isuzu hasn't just left the MU-X to gather dust – they've continuously upgraded,given it regular refreshes. We're talking tweaks to the exterior styling, sprucing up the interior with better tech, and beefing up the safety kit too. Think nice touches like Apple CarPlay and Android Auto integration, plus some advanced driver assistance systems thrown into the mix.
It's no surprise the MU-X has found a big fan base here in Malaysia. It's a hit with families who appreciate the space, and with off-road enthusiasts who trust that Isuzu reliability. When you combine its proven performance with a practical, roomy design, it's easy to see why it's a top pick in its segment. If you're in the market for a tough, no-nonsense SUV that can handle whatever you throw at it, the MU-X should definitely be on your shortlist. Do yourself a favor – head down to your nearest Isuzu dealer and take one for a spin to really get a feel for what it can do.
Q
What is the fuel consumption of Isuzu MU-X 2.5 in liters
The fuel economy of the Isuzu MU-X 2.5 can vary depending on driving conditions and vehicle setup. Official figures put its combined fuel consumption at around 7.5 to 8.5 liters per 100 kilometers, which works out to roughly 0.075 to 0.085 liters of diesel per kilometer. Of course, your actual mileage might differ based on factors like road conditions, driving style, and how much you're carrying.
Under the hood, you've got that 2.5-liter turbo diesel engine Isuzu's known for—tough as nails and packed with low-end torque, making it a solid fit for Malaysia's long highway stretches and those trickier off-road bits. Isuzu's engine tech has always had a focus on frugal fuel use, and when paired with the efficient gearbox, it helps keep those fuel costs in check.
If you're watching the pump, keeping up with regular maintenance goes a long way—stuff like swapping out the air filter and getting fresh oil changes to keep the engine running at its best. And let's not forget: easy on the throttle, avoiding sudden acceleration, that kind of smooth driving style can definitely help you squeeze more kilometers out of a tank.
The MU-X has built up a strong following in Malaysia's mid-size SUV scene, and it's not hard to see why. Beyond just reliable performance and wallet-friendly upkeep, it's got the space for the family and the off-road chops for weekend adventures. Now, if you're dead set on maximum fuel savings, you might want to check out the latest hybrid or electric SUVs. But for diesel fans, the MU-X still stands out as a practical, budget-conscious choice.
Q
What is the fuel consumption of Isuzu MU-X 1.9 car in liters
The Isuzu MU-X 1.9 is powered by the 1.9-liter Blue Power turbo-diesel engine, which has built a solid reputation for fuel efficiency. Official figures peg the combined fuel consumption at around 6.5 to 7.5 liters per 100 kilometers, though real-world numbers will naturally swing based on your driving style, road conditions, and how much you're hauling. Expect it to creep up to 8-9 liters/100km in stop-and-go city traffic, while highway cruising can see it dip to around 6 liters/100km.
This engine isn't just about sipping fuel, though. It employs common-rail injection and variable geometry turbocharging to strike a nice balance between power delivery and efficiency. With 150 horsepower and a healthy 350 Nm of peak torque on tap, it's well-suited to Malaysia's diverse road conditions, whether you're navigating city streets or heading out on the open highway.
For diesel engine care, sticking to regular oil changes and fuel filter replacements is key. Also, always use good quality, specification-compliant diesel to keep that engine running efficiently for the long haul. If you're looking to squeeze out even better fuel economy, try maintaining smooth acceleration, avoiding harsh braking, and keeping those tires properly inflated – simple habits that go a long way.
As a seven-seater SUV, the MU-X offers decent space practicality and off-road capability for its class, making it a reliable pick for family users or those who frequently hit the road for long journeys.
Q
Which type of 18 inch wheel rims tire is better to replace for Isuzu MU-X?
When it comes to tire choices for upgrading your Isuzu MU-X to 18-inch wheels, I'd recommend all-terrain (AT) tires that balance on-road comfort with off-pavement capability. Options like the Bridgestone Dueler A/T Revo 3, Toyo Open Country A/T III, or Michelin LTX Force are solid picks—they hold up well in Malaysia's tropical heat. Stick with sizes like 265/60R18 or 275/65R18 to keep the diameter within a 3% variance from stock, which helps maintain accurate speedo readings and proper gearing.
Crucial note: Make sure the new wheels' offset (ET value) matches the factory specs to avoid rubbing issues when turning or putting extra strain on the suspension. And don't skip a wheel alignment after the swap—it's a must. Since the MU-X is a body-on-frame, rugged SUV, stepping up to a taller sidewall (like the 65 aspect ratio) can really boost its off-road game by adding cushioning over rough terrain. Just be aware that chunkier tread patterns tend to generate more road noise at highway speeds—that's the trade-off for better grip off-road.
If your daily grind is mostly city driving, a highway-terrain (HT) tire like the Yokohama Geolandar H/T G056 might suit you better. Their low rolling resistance design can help eke out better fuel economy, which is always a plus. After any tire/wheel upgrade, getting PUSPAKOM certification is smart to keep things legal. Also, keep an eye on your TPMS readings regularly, and with Malaysia's frequent downpours, prioritize tires with good water evacuation grooves to maintain wet traction.
Q
What is the model of Isuzu MU-X car remote control battery
If you're wondering about the remote battery type for your Isuzu MU-X, here's the lowdown: this SUV typically uses a CR2032 coin cell battery. It's a super common size—you can grab one at just about any supermarket, hardware store, or auto parts shop without hassle. Swapping it out is a breeze too: just pop open the remote case with a coin, watch the positive/negative orientation, and drop the new battery in. No special skills needed.
Pro tip: Check your battery every 1-2 years to avoid getting stranded with a dead remote. Stashing a spare in your glove box isn't a bad idea either. For remote care, keep it dry and away from extreme heat. Warning signs it's time for a new battery? If your range starts shrinking or the buttons feel unresponsive, that's your cue.
Heads up though—battery types can vary across car brands. CR2025 or CR1632 are also pretty common, so double-check your specific model if you're unsure. If a fresh battery still doesn't fix things, your remote might need re-pairing or there could be another issue. In that case, swing by an authorized Isuzu service center—their techs have the tools and know-how to sort it out quickly.
Q
How much tax does Isuzu MU-X 1.9 need to pay
Let's break down how taxes work for the Isuzu MU-X 1.9 under Malaysia's automotive tax structure. First off, the key factors here are engine displacement, vehicle category, and whether it's imported or locally assembled. Since it's packing a 1.9-liter diesel engine – which falls into the smaller displacement bracket – you're looking at relatively lower road tax compared to bigger-engined models. Typically, you're talking somewhere between RM200 to RM400 annually, though exact figures can vary slightly depending on the state you're registering it in.
Then there's the Sales and Services Tax (SST) when you buy the new vehicle. Right now, Malaysia's standard SST rate is 10%, but here's the thing – some locally assembled models might qualify for exemptions or reductions. My advice? Always check with your nearest Isuzu dealership for the latest tax incentives before signing on the dotted line.
Malaysia's car tax system also includes import duties and excise taxes, which fluctuate based on where the vehicle is sourced from and its engine size. Getting a handle on these tax specifics will help you budget more accurately for your new ride. And let's not forget – as a diesel-powered SUV, the Isuzu MU-X 1.9 brings solid fuel efficiency and that smaller displacement advantage to the table, making it a smart pick for buyers who prioritize practicality and keeping long-term running costs in check.
Popular Cars
Model Year
Car Compare
Car Photo
Latest Q&A
Q
Do I need an alignment after rotation?
Whether a four-wheel alignment is needed after tire replacement depends on the actual condition of the vehicle. If only the tires are replaced and the vehicle has been driving normally without deviation, steering wheel vibration, or uneven tire wear, a four-wheel alignment is usually not required immediately, but wheel balancing must be performed to ensure stability when the wheels rotate at high speeds. However, if problems such as directional deviation, reduced steering precision, misaligned steering wheel, or abnormal tire wear (e.g., one-sided wear) occur after tire replacement, four-wheel alignment is necessary to adjust the geometric parameters of the suspension system (including caster angle, front wheel camber, etc.), thereby restoring the vehicle's straight-line driving stability and uniform tire contact with the road. Moreover, if chassis component repairs (such as suspension or steering system) are involved during tire replacement or the vehicle has been in a collision, four-wheel alignment becomes an essential step, as it can effectively reduce abnormal tire wear, improve handling safety, and lower fuel consumption. It is recommended to check the alignment parameters regularly every 20,000 kilometers or once a year. If you frequently encounter rough road conditions (such as curbs or speed bumps) during daily driving, the inspection interval should be shortened accordingly. Professional technicians can measure the data using specialized equipment and compare it with the manufacturer's specifications to determine whether adjustments are needed.
Q
Is it okay to rotate tires every 10,000 km?
Rotating tires every 10,000 kilometers is a reasonable and necessary maintenance measure, especially for fuel vehicles, as this frequency can effectively balance the wear difference between front and rear tires. Tire rotation involves regularly adjusting the installation positions of tires (e.g., moving front tires to the rear), which ensures more uniform wear across all tires, thereby extending the overall service life by approximately 20%-30%. For fuel vehicles, it is recommended to rotate tires every 10,000 kilometers, while for new energy vehicles, due to their greater weight and stronger torque output, the interval should be reduced to 8,000 kilometers. During rotation, the cross-rotation method should be employed (i.e., moving front tires to the opposite rear positions), and tire pressure should be checked simultaneously to ensure it meets the specified standards (2.3-2.5 bar for fuel vehicles, with an additional 0.2 bar for new energy vehicles). It is important to note that if a tire exhibits abnormal unilateral wear, bulges, or tread depth below 1.6 millimeters, simple rotation is not recommended and the tire should be replaced immediately. Regular monthly tire pressure checks and removal of debris from treads can further enhance tire performance and safety.
Q
What happens if you don't rotate tires?
If tire rotation is not performed regularly, it will lead to uneven tire wear, which in turn causes multiple problems. For front-wheel-drive vehicles, the front tires bear both driving and steering functions, so their wear rate is significantly faster than that of the rear tires; for rear-wheel-drive vehicles, since power is concentrated on the rear tires, the rear tires wear more noticeably. Long-term failure to rotate tires will shorten the overall tire life by 20%-40%—the front tires may be scrapped prematurely while the rear tires remain relatively new, resulting in resource waste. In addition, uneven wear reduces traction, particularly on wet surfaces, which can easily lead to skidding or a 10%-15% increase in braking distance, thereby elevating driving risks. Irregular wear also exacerbates tire noise and increases fuel consumption by 0.3-0.8 liters per 100 kilometers due to uneven rolling resistance. It is recommended to rotate tires every 10,000 to 15,000 kilometers. For front-wheel-drive vehicles, the cross-rotation method should be employed (left front to right rear, right front to left rear), while for rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the rear tires need to be crossed to the front. After rotation, tire pressure (the standard value typically ranges from 2.3 to 2.6 bar) should be verified and wheel balancing performed to prevent high-speed vibrations. If the tires exhibit irregular wear patterns or the tread depth falls below 1.6 mm, they should be replaced immediately. Regular tire rotation not only prolongs tire lifespan but also enhances fuel efficiency and driving safety. The cost of a single rotation is approximately 50 to 100 ringgit, substantially lower than the expense of premature tire replacement.
Q
Is it good to rotate car tires?
Tire rotation is an important maintenance measure to ensure even tire wear and extend service life. It is recommended to perform it every 5,000 to 10,000 kilometers or when uneven wear is detected. For front-wheel drive vehicles, the front tires wear faster as they handle steering and braking tasks, so they need to be cross-rotated with the rear tires (left front to right rear, right front to left rear). For rear-wheel drive vehicles, the rear tires should be diagonally swapped with the front tires to balance the wear of the drive wheels. If the tires have a directional tread pattern or asymmetric design, the rotation direction must be maintained, and only front-to-rear swaps on the same side are allowed to avoid affecting handling on wet and slippery roads. After rotation, the tire pressure should be adjusted to the standard for the corresponding wheel position, and it is recommended to perform dynamic balancing and four-wheel alignment simultaneously to optimize driving stability. Note that snow tires or studded tires cannot be rotated, and tires with different front and rear sizes can only be swapped left and right. Regular rotation can reduce abnormal wear (such as uneven wear or wavy patterns), improve grip and driving quietness, reduce safety hazards caused by tire problems, and save replacement costs in the long run. The specific operation should be based on the vehicle manual. If there is a lack of guidance, the cross-rotation method for bias-ply tires or the same-side rotation method for radial tires can be prioritized.
Q
How often should car tyres be rotated?
The replacement cycle of car tires should be determined by comprehensively considering factors such as service life, mileage, driving habits, and environmental conditions. Generally, it is recommended to replace them every 3 to 5 years or after 60,000 to 80,000 kilometers of driving, whichever comes first. As rubber products, tires deteriorate over time. Even if the mileage threshold hasn't been reached, immediate replacement is necessary when sidewall cracks, bulges appear, or tread depth falls below 1.6 mm (verifiable with a coin test) to ensure safety. Due to their heavier weight and stronger torque output, new energy vehicles experience accelerated tire wear. It is advisable to shorten the inspection interval to every six months, with urban commuting replacement mileage typically ranging from 42,000 to 56,000 kilometers. Regular tire rotation helps distribute wear evenly. For front-wheel-drive vehicles, front-to-rear rotation every 8,000 to 10,000 kilometers is recommended, while for new energy vehicles with higher front axle loads, this interval can be reduced to 6,000 to 8,000 kilometers. Additionally, maintaining cold tire pressure at 2.3 to 2.5 bar (add 0.2 bar for new energy vehicles) and avoiding aggressive maneuvers like rapid acceleration and hard braking can extend tire lifespan by 15% to 20%. Tires exceeding 6 years from their production date (identifiable via the DOT code on the sidewall) should be replaced regardless of apparent condition.
View MoreRelated News

Why are people more willing to choose Toyota Hilux instead of Isuzu D-Max?
JamesNov 3, 2025

Isuzu D-Max continues to be one of Malaysia's best-selling pickup trucks, selling 3,081 units in the first half of the year
AshleyJul 30, 2025

Reviewing the Isuzu D-MAX: Does Its Splendid Design Match Its Off-Road Capability?
RobertApr 16, 2025

Reasons Why Pickups and SUVs Are Not Suitable for Electric Drive, Industry Secrets You Must Know Before Buying
JamesFeb 14, 2025

Isuzu launches the all-new MAXFORCE engine, more powerful!
AshleyNov 15, 2024
View More















Pros
Cons