Q
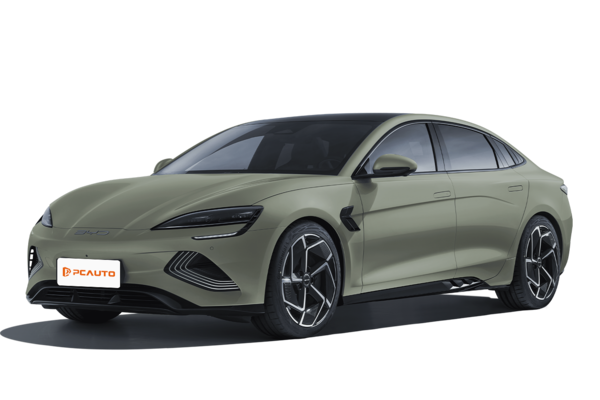
how to open byd seal frunk
To pop open the frunk on the BYD Seal, first make sure the car's unlocked. Then, hunt down the hidden release switch – it's usually tucked somewhere below the front grille, maybe near the driver's side front wheel or inside the front bumper. Give that switch a press or a pull, and the frunk lid should pop open manually. If you're struggling to find it, the owner's manual will point you in the right direction.
As an EV, the Seal's frunk is a smart extra storage spot, and it really shines in Malaysia's hot, rainy weather. It's perfect for stashing charging cables or keeping heat-sensitive stuff protected from the scorching sun. Just a heads-up though: depending on the model year or trim, the frunk release might work a bit differently. Some versions even let you unlock it remotely via the phone app, so it's worth getting to know all the ways to open it.
Oh, and don't forget to check the frunk latch mechanism regularly and keep it clean. Malaysia's dusty conditions can gunk up the works and affect how smoothly it operates over time. A little maintenance goes a long way to keeping that frunk opening like a charm.
Special Disclaimer: This content is published by users and does not represent the views or position of PCauto.
Related Q&A
Q
What is the most sold electric car in the world 2024?
As of 2024, the world's best-selling electric vehicle is the Tesla Model Y. This ride has won over consumers globally, thanks to its impressive range, cutting-edge autonomous driving tech, and that ever-expanding Supercharger network. It's been particularly killing it in North America, Europe, and Asia. For Malaysian buyers, the Model Y might just be a top contender too. Tesla's been steadily beefing up its presence in Southeast Asia, and that includes rolling out Superchargers in Malaysia. Sure, the local EV scene is still growing, but government support for new energy vehicles—think tax breaks and charging infrastructure pushes—is really helping to drive adoption.
But Tesla isn't the only player in town. Brands like BYD, Hyundai, and Nissan also hold significant chunks of the global EV market. Take the BYD Atto 3 (that's the Yuan PLUS) and Hyundai Ioniq 5, for example—they're gaining traction with their solid value for money and fresh, innovative designs.
For Malaysian consumers eyeing an EV, it pays to weigh factors like range, how easy it is to charge up, after-sales service, and local market support. With tech advancing and policies backing things up, the Malaysian EV market is only going to get more diverse in the years ahead.
Q
What is BYD ranked in the world in 2024?
BYD has solidified its position among the world's top automakers in 2024, with standout performance in the new energy vehicle sector. Industry data shows their sales have cracked the global top three, cementing their status as one of the most influential EV brands around. The secret to BYD's success? Their robust vertical integration – they develop everything in-house, from batteries and motors to electronic control systems. On top of that, they're aggressively expanding overseas, with Southeast Asia (Malaysia included) being a key strategic focus.
For Malaysian buyers, models like the Atto 3 are steadily gaining traction thanks to their strong value proposition and impressive range. Local assembly plans are only set to boost their competitiveness further. A big selling point? BYD's Blade Battery technology, which leads the industry in safety and energy density – a crucial advantage in Malaysia's hot climate.
As the global shift to electrification accelerates, BYD looks primed to grow its market share and roll out more innovative products. If you're a Malaysian considering an EV, make sure to weigh factors like charging infrastructure, warranty policies, and local after-sales support before making your decision.
Q
What is the best-selling EV in China 2024?
The best-selling electric vehicle in China's market for 2024 is the BYD Song PLUS EV. This model has won widespread favor among consumers thanks to its impressive range, spacious interior, and BYD's accumulated technological expertise in the EV sector. As a leader in China's EV market, BYD boasts a product lineup spanning from entry-level to high-end models, catering to the diverse needs of different consumers. The success of the Song PLUS EV also reflects Chinese consumers' preference for family-friendly electric SUVs.
For Malaysian consumers, while BYD might not enjoy the same level of brand recognition as Japanese or German marques in the local market, the technological prowess and cost-effectiveness advantages of Chinese brands like BYD are becoming increasingly evident as EVs gain global traction. It's plausible that they could carve out a significant presence in Malaysia in the years to come.
The development of electric vehicles doesn't solely rely on the performance of the cars themselves; the improvement of charging infrastructure is also a crucial factor driving their widespread adoption. The Malaysian government has been actively pushing for the implementation of EV-related policies in recent years, including the construction of charging stations and vehicle purchase subsidies. These initiatives will create favorable conditions for the promotion of electric vehicles in Malaysia.
Q
How many cars has BYD sold in China in 2024?
I haven't been able to track down specific, standalone figures for BYD's sales exclusively in China for 2024 just yet. However, what we do know is that BYD's global sales hit a whopping 4.27 million units last year, with overseas markets contributing 417,204 units. Doing a little back-of-the-envelope math, that roughly puts their China sales at around 3.8528 million units (4.27 million -41.7204 million=3.852796 million).
2024 was an absolutely stellar year for BYD. They didn't just dominate the sales charts in China; they also clinched the title of the world's top-selling new energy vehicle manufacturer. A big part of their success comes down to their multi-brand strategy – think "BYD," "Fang Cheng Bao," "Denza," and "Yangwang" – each catering to different market segments and needs. On top of that, continuous technological innovation, like their "e-platform 3.0 Evo" and "5th Generation DM Technology," has been a major driver propelling those sales numbers ever higher.
Q
How much is the BYD Seal in 2024?
The 2024 BYD Seal comes in multiple variants with different price tags. Specifically, the BYD Seal Dynamic EV is priced at RM 163,800, the BYD Seal Premium (Extended Range) goes for RM 179,800, and the top-of-the-line BYD Seal Performance AWD hits RM 199,800. All these are pure electric D-segment sedans, boasting solid range and equipment levels. Let's talk dimensions: they stretch 4,800mm in length, 1,875mm in width, 1,460mm in height, with a 2,920mm wheelbase. There's seating for five, and a 400-liter trunk to boot. Performance-wise, the variants differ quite a bit. The Seal Performance AWD, for example, rockets from 0-100km/h in a claimed 3.8 seconds, while the Seal Dynamic EV does the same sprint in a stated 7.5 seconds. So, buyers can pick the one that best fits their needs.
Q
What Segment Does BYD Seal Belong to?
The BYD Seal belongs to the D-segment cars. D-segment cars are typically mid to large-sized vehicles, well-known for striking a balance between space, comfort, and performance.
The BYD Seal has a body length of 4,800 millimeters, a width of 1,875 millimeters, and a wheelbase of 2,920 millimeters, offering passengers a relatively spacious interior. The trunk space is also quite decent. Such specification makes it suitable for comfortable long - distance trips and can meet the sufficient space requirements for daily use. Moreover, in terms of performance, the Seal provides different versions with various power outputs. It can provide a smooth daily driving experience and also offer a more exciting high - performance driving feel. Whether for family users or individual users who desire more space and better performance in their vehicles, the D - segment BYD Seal is an appealing choice.
Q
What's the Reslae Value of BYD Seal?
The BYD Seal, a relatively new electric vehicle in the Malaysian market, currently lacks complete data on its resale value, but general resale value for EVs can provide some references. Due to rapid advancements in EV technology, the resale value of electric vehicles typically declines slightly faster than that of comparable internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles in the first three years—around 50%-60% for EVs versus 60%-70% for ICE cars.
Key factors influencing resale value include battery health (BYD offers an 8-year/160,000 km battery warranty), growing brand recognition (BYD has shown strong performance in recent years), and the maturity of EV infrastructure (such as charging network development). Compared to similar ICE vehicles, the BYD Seal's extended battery warranty and lower operating costs (electricity being significantly cheaper than fuel) may help mitigate depreciation.
For prospective buyers, it is advisable to consider certified pre-owned programs and maintain complete service records to preserve resale value. As EV adoption increases, more definitive resale value data will be provided.
Q
What's the Displacement of BYD Seal?
The BYD Seal is an electric vehicle, so it doesn't use the traditional "CC" (cubic centimeters, used to measure internal combustion engine displacement) as a metric. It provides different versions, such as the Dynamic EV, Premium (Extended Range), and Performance AWD. In terms of the powertrain, the Dynamic EV version has a total motor power of 150kW, a maximum horsepower of 204PS, and a total torque of 310N·m. The Premium (Extended Range) version has a total motor power of 230kW, a maximum horsepower of 308PS, and a torque of 360N·m. The Performance AWD version is more powerful, with a combined system power of 390kW, a combined horsepower of 523PS, and a combined torque of 670N·m. These motors can provide efficient and strong power output, meeting different consumers' needs for speed, range, etc. Moreover, the all - electric drive also complies with the current trend of environmental protection and energy conservation.
Q
What's the PCD Size of BYD Seal?
The PCD (Pitch Circle Diameter) of the BYD Seal is 5×114.3, which means the wheel hub has 5 bolt holes evenly distributed on a circle with a diameter of 114.3 millimeters, matching the standard used by many mainstream Japanese vehicles (such as Honda and Toyota). So, it's easy to find compatible wheel hub options for modification or replacement in the Malaysian market.
Beyond PCD, wheel modifications also require attention to other parameters, including the hub bore (recommended to use OEM-concentric hub rings for precise fitting), offset (ET value), and wheel width to avoid affecting suspension geometry or causing friction. For wheel upgrades, it is advisable to choose EV-rated products that can accommodate the Seal's battery weight and prioritize purchasing through BYD-certified channels to ensure safety and compatibility.
Q
Does BYD Seal Support Apple Carplay?
The BYD Seal doesn't have the Apple CarPlay feature. Apple CarPlay is a system developed by Apple Inc., which allows iPhone users to connect their devices to the in-vehicle infotainment system. Although some car models in the market support this feature, the BYD Seal isn't one of them.
However, the BYD Seal has its own advanced infotainment system. It's equipped with a 15.6 - inch intelligent rotating touchscreen, which can provide a wide range of entertainment and vehicle control functions. This car also adopts a comprehensive set of standard configurations, such as various safety systems, comfortable seats with multiple adjustment options, and a high - quality sound system with 12 Dynaudio speakers. Even though the Seal doesn't have Apple CarPlay, its own infotainment capabilities can still bring users a convenient and pleasant driving experience.
Popular Cars
Model Year
Car Compare
Car Photo
Latest Q&A
Q
Which tyre is best for mileage?
For tire choices focused on high mileage performance, Michelin Primacy 5 and Maxxis series are two top options worthy of priority consideration. Michelin Primacy 5 employs MaxTouch technology to optimize force distribution, paired with a tread design that increases porosity by 10%. Tests demonstrate it delivers 24% more mileage than comparable high-end products while maintaining excellent wet braking performance even when worn. The retail price for 16 to 19-inch sizes ranges from 477 to 1,026 Ringgit. Maxxis tires are renowned for their cost-effectiveness. Models such as MA510 utilize high-strength rubber and reinforced shoulder technology to ensure even wear under challenging road conditions. User feedback indicates tread depth remains compliant after 40,000 kilometers for certain vehicle models, with a typical service life of 3-5 years. Note that actual tire mileage is significantly influenced by driving habits—rapid acceleration or frequent overloading will reduce longevity. Regular checks of tire pressure and wear patterns are recommended to optimize value. For balanced performance, Michelin Primacy 5's quiet rib technology additionally enhances comfort, whereas Maxxis MA202's symmetrical tread design ensures stable handling on both dry and wet surfaces. Both brands have obtained international certifications guaranteeing reliability.
Q
Which is better Bridgestone or Yokohama?
As two major high-end tire brands in Japan, Bridgestone and Yokohama each have their own advantages in performance and technology. The Bridgestone Potenza Sport A/S features an asymmetric tread design, making it suitable for sports cars and crossovers with 16 to 20-inch wheels. It delivers excellent grip and handling in various weather conditions year-round, and its overall score of 9.1 out of 10 reflects outstanding wear resistance and wet-road performance. The Yokohama Advan Sport A/S Plus, meanwhile, is renowned for its innovative tread pattern and orange oil compound, particularly suited for luxury performance vehicles, and excels in noise reduction and eco-friendly material applications. In terms of market positioning, both are mid-to-high-end products, but Bridgestone boasts a more extensive local after-sales network, while Yokohama's ADVAN series is more popular among car modification enthusiasts. For selection advice: choose Bridgestone for comprehensive durability and sporty performance, or opt for Yokohama if prioritizing quiet comfort or environmental features. Both brands typically fall within the RM800 to RM2500 price range, depending on size and model.
Q
What is suspension and types?
The suspension system is a key component connecting the wheels and the vehicle body, primarily responsible for cushioning road impacts, maintaining body stability, and enhancing handling performance. Common suspension types are divided into two main categories: independent and non-independent. Among independent suspensions, the MacPherson strut is the most prevalent, featuring a simple structure, low cost, and compact design, and is widely used in the front wheels of front-wheel-drive compact cars. Double-wishbone and multi-link suspensions are more commonly found in mid-to-high-end models; by utilizing multiple links to precisely control wheel trajectories, they significantly improve handling and comfort, though at higher manufacturing costs. Non-independent suspensions such as torsion beam suspensions, owing to their compact structure and low cost, are frequently employed in the rear wheels of economy cars, albeit with slightly inferior comfort. Additionally, advanced systems like air suspension and electromagnetic suspension can adjust suspension characteristics in real time by regulating air pressure or electric current, and are predominantly used in luxury models to balance dynamic performance and ride quality. When selecting a vehicle, consumers can make choices based on their budget and requirements; for instance, family cars typically prioritize a combination of MacPherson struts and torsion beam suspensions, while performance or luxury vehicles often favor multi-link or air suspensions.
Q
Which tyre brand lasts longer?
In the Malaysian market, tire brands with outstanding durability include Giti, Michelin, and Maxxis. Giti tires utilize reinforced cord fabric and an optimized rubber compound. Its Comfort T29 series demonstrates an 80% improvement in wear resistance and offers an 80-kilometer run-flat capability, making it suitable for daily driving with excellent cost-effectiveness. The Michelin Primacy 5 employs MaxTouch technology to evenly distribute stress, claiming 24% greater mileage than comparable premium brands and a 13% reduction in braking distance on worn wet surfaces. Available in 16-19 inch sizes, these tires range from 477 to 1026 Malaysian Ringgit. Maxxis tires feature a standard service life of 60,000-80,000 km (approximately 5-7 years), with real-world testing showing less than 15% wear after 8 years of use. Their patented tire pressure monitoring system effectively mitigates abnormal wear risks. Additionally, Bridgestone is renowned for extended tread longevity, while Continental delivers consistent performance in both dry and wet conditions. Yokohama tires combine eco-friendly materials with wear-resistant properties. Selection should account for driving habits, road conditions, and budget. Regular tire pressure checks (monthly when cold) and maintaining tread depth (minimum 1.6mm) significantly prolong tire lifespan.
Q
Who is better, Bridgestone or Michelin?
As global top-tier tire brands, Bridgestone and Michelin each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on specific needs. Bridgestone excels in wear resistance and durability, making it suitable for long-distance driving or heavy-duty vehicles. Its tire sidewall design enhances grip and high-speed stability, and its fuel efficiency is also outstanding, though its comfort level is relatively moderate. Michelin, on the other hand, is renowned for its noise-reduction technology and soft tread, delivering superior driving comfort. Particularly in models tailored for luxury vehicles such as the Primacy 4+, its wet braking, hydroplaning resistance, and wear performance have received professional acclaim, though its wear resistance is slightly weaker and the price is higher. If you prioritize cost-effectiveness and durability, Bridgestone is a pragmatic choice; if you value quietness and comprehensive safety performance, Michelin holds more advantages. It is advisable to make a decision based on the vehicle's purpose (e.g., daily commuting or long-haul transport) and budget, while prioritizing the recommended compatible models from local authorized dealers to ensure optimal performance.
View MoreRelated News

2025 BYD Seal Coming to Malaysia with DiSus-C Adaptive Suspension
JohnAug 13, 2025

BYD Seal interior design revealed: A fusion of modern technology and luxury
RobertJul 15, 2025

Photos of the BYD Seal 06 Touring Edition Reveal the Brand's Entry into a New Niche Market
JamesMar 24, 2025

BYD Wins Japan's Annual EV Award Again with Seal
MichaelMar 6, 2025

BYD Seal 05 DM-i Declaration Image Revealed: Fifth Generation DM Technology, 1.5L Hybrid System!
Kevin WongDec 10, 2024
View More

















Pros
Cons